As fall brings cooler temperatures and stunning landscapes, it’s the perfect season to head outdoors and stay active. For individuals with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D), regular physical activity isn’t just about fitness—it’s also an effective way to help manage blood sugar and support overall health. Outdoor activities can boost mood, reduce stress, and improve physical well-being, all of which are especially beneficial for people managing T1D. An exciting advancement in diabetes technology is the automated insulin delivery device, which simplifies insulin management and improves glycemic control. With a few mindful strategies, anyone with T1D can enjoy the season while keeping their health in check.
Ready to embrace the outdoors this fall?Learn how DRC’s research is helping those with T1D stay active and live healthier lives.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
T1D is a chronic autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Insulin is a crucial hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. This form of diabetes mellitus requires individuals to manage their blood sugar levels through insulin therapy.
T1D is often diagnosed in children and young adults, but it can occur at any age. The exact cause remains unknown, though it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Common symptoms include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. If not properly managed, T1D can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) is an advanced method for insulin delivery that offers more precise insulin administration compared to traditional injection methods.
Understanding the nature of T1D and the importance of insulin therapy is essential for effective management. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and adherence to prescribed insulin doses are critical to maintaining good health and preventing complications.
The Health Benefits of Staying Active with Type 1 Diabetes
Staying active offers numerous benefits for everyone, but it can be particularly helpful for people living with T1D. Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, meaning that your body uses insulin more effectively, which helps keep blood sugar levels stable. Exercise also plays a role in cardiovascular health, which is a critical factors in diabetes care.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) helps in real-time monitoring of blood glucose levels, thereby aiding in maintaining stable blood sugar levels during physical activity.
Beyond physical health, regular exercise has mental and emotional benefits too. Studies show that physical activity can improve mood, reduce anxiety, and enhance sleep quality. These benefits are particularly important for individuals with T1D, as stress and sleep issues can negatively impact blood sugar management. The fall season, with its moderate temperatures, offers an inviting time to explore these benefits without the heat of summer or the chill of winter.
Fun Fall Activities to Stay Active
Fall offers countless outdoor activities that are perfect for staying active while enjoying the beauty of the season. Here are a few T1D-friendly activities, along with tips for keeping blood sugar levels balanced:
- Hiking: Hitting the trails is an excellent way to engage in aerobic exercise while enjoying fall foliage. Hiking is adaptable in terms of pace and difficulty, making it suitable for people of all fitness levels. Always bring a blood glucose meter, snacks, and water, and remember to check your blood sugar at intervals. Using a continuous glucose monitor can help regularly check blood sugar levels during the activity. Additionally, an insulin pump can automate insulin delivery, adjusting for basal rates and boluses, which simplifies management during hikes.
- Cycling: Fall’s cooler air is perfect for a bike ride. Cycling provides both cardiovascular benefits and an easy way to vary intensity, whether you prefer a leisurely ride or a more challenging route. Be sure to carry a small bag with water, a glucose meter, and some fast-acting carbs in case of a sudden drop in blood sugar.
- Walking in Nature Parks: If you prefer a gentler activity, walking through a park is a wonderful option. Walking helps regulate blood sugar with a lower risk of sudden drops, especially when done at a steady pace. Bring a friend or family member along to enjoy the scenery together.
- Outdoor Games: For a fun way to stay active, consider playing football, frisbee, or other outdoor games with friends or family. These games combine moderate cardio exercise with social interaction, which can uplift mood and add enjoyment.
Each of these activities can be adjusted based on individual needs, so it’s essential to listen to your body, monitor your levels, and make adjustments as necessary.
Support research that helps people with T1D live healthier lives by staying active. Discover how DRC’s research makes a difference.
Managing T1D with Continuous Glucose Monitoring During Physical Activity
Successfully managing T1D while staying active in the fall requires careful planning and regular monitoring of your blood glucose level. Here are a few tips to help keep blood sugar levels stable:
Monitor Blood Sugar: It’s essential to check your blood glucose level before, during, and after physical activity. Monitoring at different points helps identify patterns in how your body responds to different activities and intensities. Additionally, using insulin pumps can provide more precise insulin delivery, enhancing diabetes management during physical activities.
Adjust Insulin and Carbohydrate Intake: Depending on the activity and duration, you may need to adjust insulin dosage or eat additional carbohydrates. More intense activities often require more frequent checks and adjustments, so prepare in advance and have fast-acting carbs on hand for immediate energy.
Carry Essentials: Always pack a small bag with a glucose meter, fast-acting carbs (like glucose tablets or fruit juice), and plenty of water. Staying hydrated is essential, as dehydration can impact blood sugar levels. Also, consider having a friend or family member accompany you, especially for longer or more intense activities.
These simple strategies can help you manage T1D effectively while reaping the benefits of physical activity. With regular monitoring and thoughtful preparation, you can enjoy an active fall season without compromising on your health.
Monitoring Blood Glucose
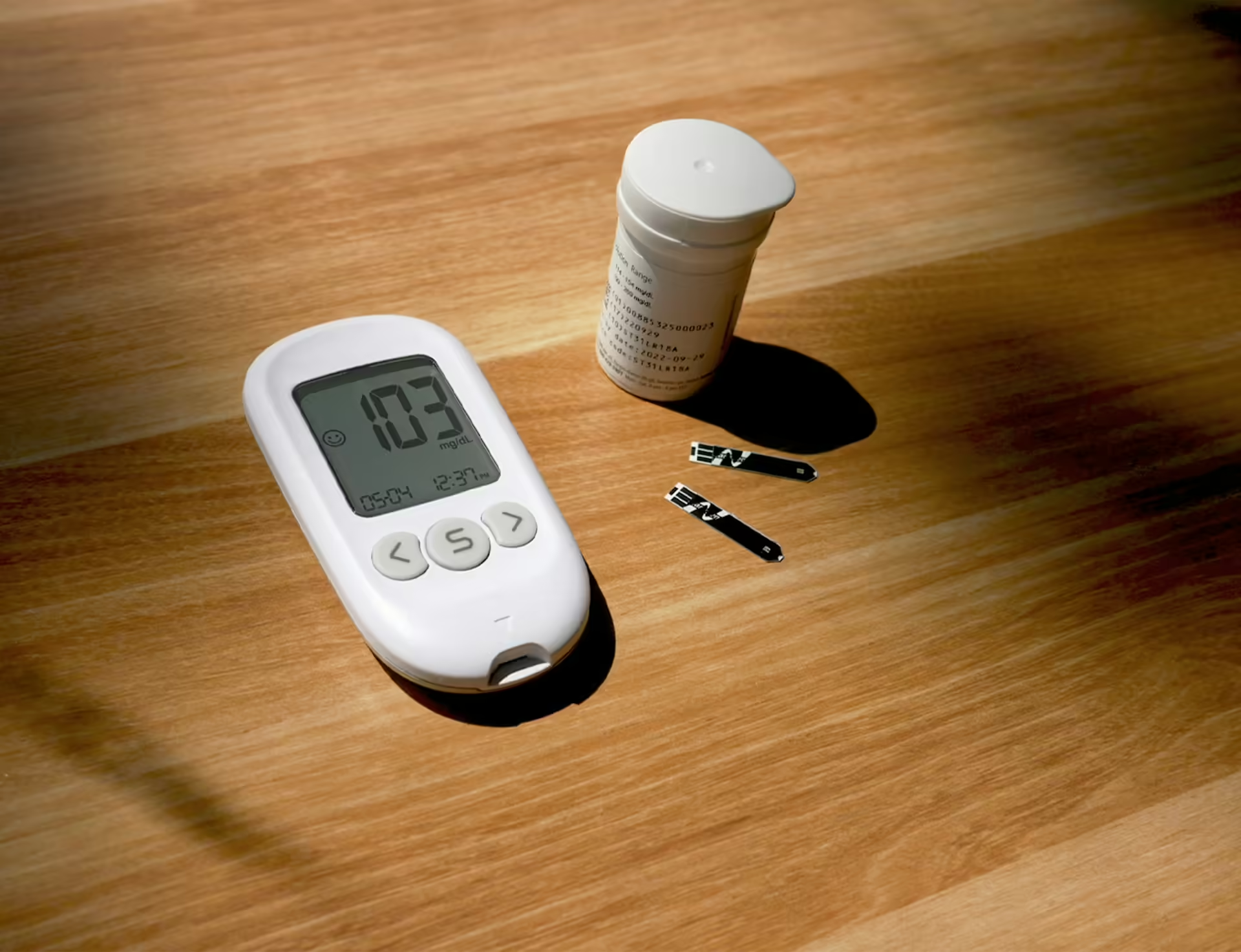
Monitoring blood glucose levels is a cornerstone of managing Type 1 Diabetes. It involves regularly checking the level of glucose in the blood using a blood glucose meter or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). A blood glucose meter is a small electronic device that measures glucose levels from a drop of blood, typically obtained by pricking the finger. A CGM, on the other hand, is a device inserted under the skin that continuously measures glucose levels throughout the day.
The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with T1D check their blood glucose levels at least four times a day, including before meals, before bedtime, and before exercise. Regular monitoring helps in:
- Adjusting insulin doses to achieve optimal blood glucose control.
- Identifying patterns and trends in blood glucose levels.
- Making informed decisions about diet and exercise.
- Preventing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
By keeping a close eye on blood glucose levels, individuals with T1D can better manage their condition and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Healthy Eating and Carbohydrate Management
Healthy eating plays a pivotal role in managing Type 1 Diabetes. Balancing carbohydrate intake with insulin doses is key to maintaining stable blood sugar levels. The American Diabetes Association recommends a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods, including vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limiting added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates is also advised.
Carbohydrate counting is an effective tool for managing blood sugar. By tracking the amount of carbohydrates in each meal and snack, individuals with T1D can adjust their insulin doses accordingly. Using a blood glucose meter to monitor blood sugar levels helps in making necessary adjustments to both diet and insulin therapy.
Incorporating these dietary strategies can significantly improve glycemic control, making it easier to manage T1D and enjoy a healthier lifestyle.
Understanding Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are a vital part of a healthy diet, but they can significantly impact blood glucose levels. Understanding how carbohydrates affect blood glucose is crucial for managing Type 1 Diabetes.
Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose during digestion, which then enters the bloodstream. The amount and type of carbohydrates consumed can influence the rate and extent of glucose absorption, affecting blood glucose levels. The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood glucose levels. Foods with a high GI, like white bread and sugary snacks, cause rapid increases in blood glucose, while low GI foods, such as whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, lead to more gradual rises.
Individuals with T1D need to consider the carbohydrate content of their meals and snacks to adjust their insulin doses accordingly. Working with a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator can help develop a personalized meal plan that balances carbohydrate intake with insulin requirements, promoting better blood glucose control.
Managing Blood Glucose Levels During Exercise
Exercise is an essential component of a healthy lifestyle, but it can also affect blood glucose levels. Managing blood glucose during exercise is crucial for individuals with Type 1 Diabetes to prevent hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
The American Diabetes Association recommends checking blood glucose levels before, during, and after exercise to ensure they are within a safe range. Here are some tips to help manage blood glucose levels during physical activity:
- Check blood glucose levels before exercise to ensure they are within a safe range (usually between 100-180 mg/dL).
- Adjust insulin doses and carbohydrate intake based on the type and duration of exercise.
- Monitor blood glucose levels during exercise to prevent hypoglycemia.
- Consume carbohydrates or glucose tablets as needed to prevent low blood sugar.
- Adjust insulin doses and carbohydrate intake after exercise to prevent high blood sugar.
By following these guidelines, individuals with T1D can enjoy the benefits of exercise while maintaining stable blood glucose levels.
Coping with Type 1 Diabetes
Living with Type 1 Diabetes can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Effective management requires a combination of self-care, stress management, and problem-solving skills. Regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, is recommended by the American Diabetes Association to help manage blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
Stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga, can also be beneficial. These practices help reduce anxiety and improve emotional well-being, which is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Joining a support group or online community can provide additional support and empowerment. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can offer valuable insights and encouragement, making it easier to navigate the challenges of living with T1D.
By adopting these coping strategies, individuals with T1D can better manage their condition and lead fulfilling, active lives.
Emotional Challenges of Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Living with Type 1 Diabetes can be emotionally challenging, and it’s important to address these challenges to maintain good mental health. The emotional aspects of T1D can include:
- Anxiety and stress related to managing blood glucose levels and preventing complications.
- Fear of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
- Feelings of guilt and shame related to food choices and insulin management.
- Social isolation and stigma associated with having a chronic illness.
- Depression and anxiety due to the ongoing burden of managing T1D.
Fall is the perfect season to stay active and enjoy the outdoors, and with the right planning, those with Type 1 Diabetes can participate fully and safely. By monitoring blood sugar, carrying essential supplies, and choosing enjoyable activities, you can manage T1D effectively and gain all the benefits of physical activity. Ongoing research, such as efforts focused on Reversing Type 1 Diabetes Without Insulin Replacement, offers hope for even greater management options in the future.
Seeking support from mental health professionals, joining support groups, and utilizing online resources can be beneficial. It is important to prioritize mental health and seeking help when needed to manage the emotional challenges of living with T1D. By addressing these emotional aspects, individuals with T1D can improve their overall well-being and better manage their condition.
Embrace Fall and Support T1D Research
Support the Diabetes Research Connection’s mission to improve life for those with T1D by funding research that addresses these specific needs. Every bit of research brings us closer to solutions that enable individuals with T1D to live healthier, more active lives.
This fall, help DRC advance T1D research.Donate or share awareness about the impact of exercise on diabetes management at Diabetes Research Connection.