Month: January 2015
-
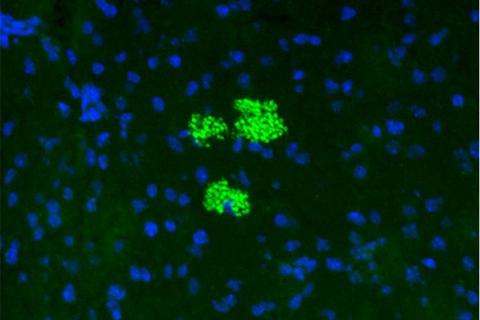
Steering Stem Cell Trafficking Into Pancreas Reverses Type 1 Diabetes
Researchers develop ‘GPS’ method to guide mesenchymal stem cells to inflammatory sites. Researchers at Harvard-affiliated Brigham…

Researchers develop ‘GPS’ method to guide mesenchymal stem cells to inflammatory sites. Researchers at Harvard-affiliated Brigham…
[give_form id=”3302″ show_title=”true” show_goal=”true” show_content=”above” display_style=”reveal”]
Accessibility Tools
